
Whole blood samples were also obtained from the 36 cows kept on a farm in field conditions. Sixty-two paired-point whole blood samples were obtained from three cows with hypocalcemia experimentally induced by Na2-EDTA infusion. Aims of present studies was to compare the commercially available ion-selective electrode handheld iCa meter (bovine blood iCa checker) with the benchtop blood gas analyzer GEM premier 3500 and handheld analyzer i-STAT 1. Point-of-care (POC) devices that veterinary practitioners can use to easily and rapidly measure blood ionized calcium (iCa) levels in cows immediately after withdrawing a blood sample on the dairy farm are needed. Clinical testing of PrismaLung+ is warranted to further characterize its performance. The newly developed PrismaLung+ performed more effectively than PrismaLung, with performance of CO2 removal comparable to A.L.ONE at the flow rates tested, despite the smaller membrane surface area of PrismaLung+ versus A.L.ONE. The resistance to blood flow across the test device, as measured by pressure drop, varied as a function of blood flow rate, and was greatest for PrismaLung and lowest for the A.L.ONE device. A Bland-Altman plot demonstrated that the CO2 infusion method was comparable to the blood gas analysis method for calculating CO2 removal. CO2 removal rates were 73 ± 4.0, 44 ± 2.5, and 72 ± 1.9 mL/min, for PrismaLung+, PrismaLung, and A.L.ONE, respectively, at QB 300 mL/min and pinCO2 45 mmHg. The PrismaLung+ device performed similarly to the A.L.ONE device, with both devices demonstrating CO2 removal rates ~ 50% greater than the PrismaLung device. The amount of CO2 removed by each device was assessed by measurement of the CO2 infused to maintain circuit equilibrium (CO2 infusion method) and compared with measured CO2 concentrations in the inlet and outlet of the CO2 removal device (blood gas analysis method). The efficacy of each device was measured at varying pCO2 inlet (pinCO2) levels (45, 60, and 80 mmHg) and blood flow rates (QB) of 200-450 mL/min the PrismaLung+ and A.L.ONE devices were also tested at a QB of 600 mL/min. The in vitro CO2 removal capacity of the PrismaLung+ (surface area 0.8 m2, Baxter) was compared with the PrismaLung (surface area 0.35 m2, Baxter) and A.L.ONE (surface area 1.35 m2, Eurosets) devices, using a closed-loop bovine blood-perfused extracorporeal circuit. We evaluated the in vitro CO2 removal capacity of the novel PrismaLung+ ECCO2R device compared with two existing gas exchangers. Advances in extracorporeal CO2 removal (ECCO2R) technologies may facilitate more protective lung ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome, and enable earlier weaning and/or avoid invasive mechanical ventilation entirely in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations.
Invasive mechanical ventilation is lifesaving in the setting of severe acute respiratory failure but can cause ventilation-induced lung injury. In particular, the i‐STAT predicted hypocalcemia with a high sensitivity. ICa²⁺ concentrations in bovine blood measured with the i‐STAT agreed with those of the Radiometer ABL800 FLEX. The Bland‐Altman difference plot revealed no bias between the i‐STAT and the Radiometer ABL 800 FLEX. The deviation from the identity line was not significant (P = 0.64). The Passing‐Bablok regression equation that fit the iCa²⁺ concentration as measured with the i‐STAT (Y) and the Radiometer ABL800 FLEX (X), was Y = −0.108276 + 1.103448 × X, with a residual deviation of 0.02. The i‐STAT performance was evaluated at two different cutoff values for iCa²⁺ concentrations (<1.00 and <1.18 mmol/L) using the receiver operating characteristic curve. The Radiometer ABL800 FLEX was the reference method and the i‐STAT was the test method. Data were subjected to Passing‐Bablok regression and Bland‐Altman plots. Venous blood samples were run on the i‐STAT and the Radiometer ABL800 FLEX for determination of blood iCa²⁺ concentrations.

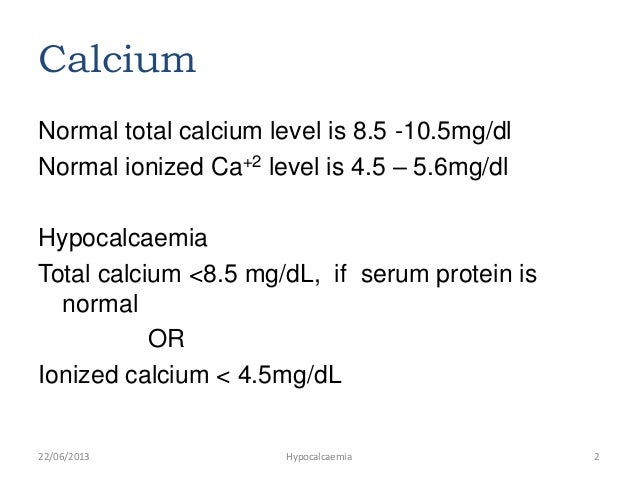
In this study, 121 cattle with various diseases were used. The primary goal of this study was to evaluate the agreement of the i‐STAT against a traditional bench‐top blood gas analyzer (Radiometer ABL800 FLEX) in the measurement of iCa²⁺ in the blood of cattle with various disorders. Information regarding the performance of the i‐STAT, a point‐of‐care analyzer, to determine ionized calcium (iCa²⁺) concentration in bovine blood is limited.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
